BioCeuticals
BioCeuticals Folinic Acid 120 caps
BioCeuticals Folinic Acid 120 caps
Couldn't load pickup availability
Bioactivated B9
BioCeuticals Folinic Acid 120 caps
Sizes: 120 capsules
BioCeuticals Folinic Acid Summary:
- BioCeuticals Folinic acid is an alternative form of folic acid that bypasses some of the steps in the conversion of folic acid to the active form, 5-methyltetrahydrofolate (5-MTHF).
- BioCeuticals Folinic acid supports healthy methylation pathways, homocysteine metabolism, DNA replication and foetal development.
BioCeuticals Folinic Acid has No Added Dairy, No Added Gluten, No Added Shellfish, No Added Soy Protein
Pregnancy Friendly, Vegan Friendly, Vegetarian Friendly
BioCeuticals Folinic Acid AUST L 233205
Dose
Dose: BioCeuticals Folinic Acid
Adults: Take 1 capsule once daily or as directed by your health professional.
Features
Features: BioCeuticals Folinic Acid
- Supports healthy methylation pathways in the body.
- Supports healthy homocysteine metabolism.
- Involved in the synthesis of S-adenosylmethionine (SAMe).
- Helps form red blood cells.
- Supports a healthy brain and nervous system function.
- Helps support cognitive health, with healthy neural development, growth and repair.
- Involved in growth and cellular replication, and contributes to normal growth of the foetus.
- Vegetarian and vegan friendly.
Ingredients
Ingredients: BioCeuticals Folinic Acid
| Each BioCeuticals Folinic Acid capsule contains: | |
| Calcium folinate | 694mcg |
| equiv. folinic acid (activated vitamin B9) | 500mcg |
Ingredient Summary
Ingredient Summary: BioCeuticals Folinic Acid
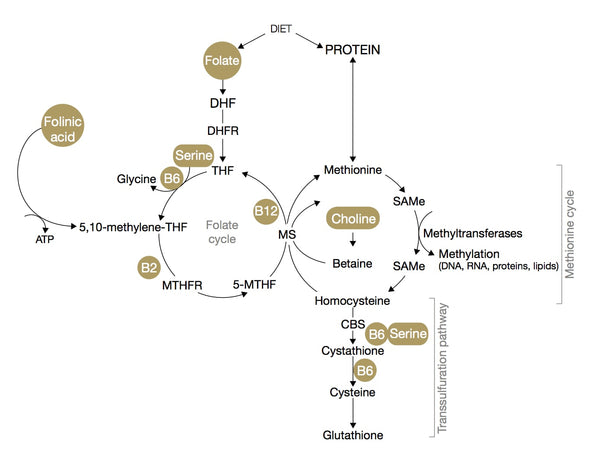
Methylation pathways and homocysteine metabolism
Folinic acid is an active metabolite of folic acid and does not require the enzyme dihydrofolate reductase (DHFR) to participate in reactions utilising folates.
The remethylation pathway of the methylation cycle actually involves methylation, re-methylation and de-methylation reactions involving folate, B12 and B2. By supplementing with folinic acid (5-formyl-THF), a number of reduction steps can be bypassed to convert directly to 5,10-methylene-THF, alleviating the need for the DHFR enzyme.
Supplementing with folinic acid, therefore, assists 5,10-methylene-tetrahydrofolate reductase (MTHFR) enzyme to produce active folate (5-MTHF) which then methylates homocysteine; helping to convert homocysteine to methionine and then SAMe, rather than elevating.
Low serum folate and elevated levels of homocysteine are associated with increased risk of developing a number of conditions.[1-10]
Cognitive health
Low folate is associated with a degree of cognitive decline.[6-8] A randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled study of 818 participants found that folic acid supplementation for three years significantly improved domains of cognitive function that tend to decline with age. Serum folate increased by 576% and plasma total homocysteine decreased by 26% in the folic acid group. The three-year change in memory, information processing speed and sensorimotor speed were also significantly better in the folic acid group.[9]
DNA replication and foetal development
Folic acid is involved in intracellular metabolism and DNA synthesis.[10]
The need for folate is higher when cell turnover is increased, such as in pregnancy and foetal development. A daily dose of 500mcg of folinic acid or folate taken one month before conception and during pregnancy may reduce the risk of women having a child with birth defects of the brain or neural tube defects such as spina bifida and anencephaly.
Methylation/remethylation and transsulfuration
Warnings
Warnings: BioCeuticals Folinic Acid
- If symptoms persist talk to your health professional.
- Do not exceed the stated dose except on medical advice.
- If you have had a baby with neural tube defect/spina bifida – seek specific medical advice.
- If you have any pre-existing conditions, are on any medications, always talk to your health professional before use.
- Some products should be ceased at least two weeks before any elective surgery, please confirm with your health professional.
- Vitamin supplements should not replace a balanced diet.
- Always read the label. Use only as directed.
- If you have any pre-existing conditions, are on any medications, always talk to your health professional before use.
- Some products should be ceased at least two weeks before any elective surgery, please confirm with your health professional.
Companion Products
Companion Products: BioCeuticals Folinic Acid
- BioCeuticals CardioNutrients Forte
- BioCeuticals CardioPack
- BioCeuticals Methyl-Max
- BioCeuticals InNatal
References
References: BioCeuticals Folinic Acid
[1] Refsum H, Ueland PM, Nygard O, et al. Homocysteine and cardiovascular disease. Ann Rev Medicine 1998;49:31-62.
[2] Seshadri S, Beiser A, Selhub J, et al. Plasma homocysteine as a risk factor for dementia and Alzheimer’s disease. N Engl J Med 2002;346(7):476-483.
[3] Moschiano F, D’Amico D, Usai S, et al. Homocysteine plasma levels in patients with migraine with aura. Neurol Sci 2008;29 Suppl 1:S173-S175.
[4] Rochtchina E, Wang JJ, Flood VM, et al. Elevated serum homocysteine, low serum vitamin B12, folate and age related macular degeneration: the Blue Mountains eye study. Am J Ophthalmol 2007;143(2):344-346.
[5] van Wijingaarden JP, Doets EL, Szczecinska A, et al. Vitamin B12, folate, homocysteine, and bone health in adults and elderly people: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Nutr Metab 2013;2013:486186.
[6] Gallucci M, Zanardo A, Bendini M, et al. Serum folate, homocysteine, brain atrophy, and auto-CM system: the Treviso Dementia (TREDEM) study. J Alzheimers Dis 2013:PMID 24028866 [Epub ahead of print].
[7] Tucker K, Qiao N, Scott T, et al. High homocysteine and low B vitamins predict cognitive decline in aging men: the Veterans Affairs normative aging study. Am J Clin Nutr 2005;82:627-635.
[8] Herrmann W, Obeid R. Homocysteine: a biomarker in neurodegenerative diseases. Clin Chem Lab Med 2011;49(3):435-441.
[9] Durga J, van Boxtel MPJ, Schouten EG, et al. Effect of 3-year folic acid supplementation on cognitive function in older adults in the FACIT trial: a randomised, double blind, controlled trial. Lancet 2007;369: 208-216.
[10] Higdon J. An evidenced-based approach to vitamins and minerals. New York: Thieme, 2003.
[11] Folic acid/folinic acid. Natural Medicines Comprehensive Database. Viewed 22 Nov 2013, www.naturaldatabase.com
[12] Braun L, Cohen M. Herbs and natural supplements: an evidence-based guide, 3rd ed. Sydney: Churchill Livingstone Elsevier, 2010.
Share